Sleepysneezeydopeydoc-blog - Physics Nerd

More Posts from Sleepysneezeydopeydoc-blog and Others


Suicide Slabs | A blog dedicated to 1961 - 1969 Lincoln Continentals






{ insp. }

Click for more vintage cars, hot rods, and kustoms
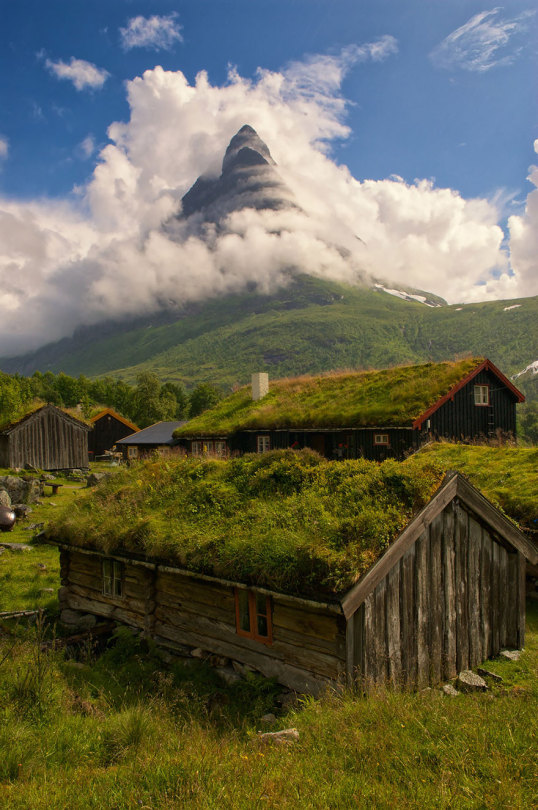











Fairlytale Scandinavian Green Roofs
Scandinavians are serious about their green roofs. They’ve had them for a while now and it doesn’t look like they’re going anywhere. They even have a competition every year to determine the best green roof project in Scandinavia by the Scandinavian Green Roof Association! But there is a reason why Scandinavians like these green roofs so much… They are not only a beautiful feature for a house, but they also offer numerous social, environmental and financial benefits. They absorb rainwater, reduce winter heating costs, reduce summer air-conditioning costs, provide insulation, and are long lasting - just to name a few.
Images and text via

“In 1972, Edward Lorenz gave a presentation titled: “Predictability: Does the flap of a butterfly’s wings in Brazil set off a tornado in Texas?” The term “butterfly effect” was born. Lorenz, who was born on this day in 1917, was a pioneer of chaos theory, which analyzes how subtle changes in the initial conditions of a system can lead to widely differing outcomes. This 2013 Physics Today article examines Lorenz and the birth of chaos theory.” - Physics Today
Chaos at fifty by Adilson E. Motter and David K. Campbell is an article that lays out the discovery of chaos. I found it a very satisfying and informative read about dynamical systems, the butterfly effect, bifurcations, predictability and fractals. You should probably go check it out by clicking on the bolded title. 👍
“Chaos sets itself apart from other great revolutions in the physical sciences. In contrast to, say, relativity or quantum mechanics, chaos is not a theory of any particular physical phenomenon. Rather, it is a paradigm shift of all science, which provides a collection of concepts and methods to analyze a novel behavior that can arise in a wide range of disciplines.” - Chaos at fifty
Image above: “The Lorenz attractor, as revealed by the never-repeating trajectory of a single chaotic orbit. The spheres shown here represent iterations of the so-called Lorenz equations, calculated using the original parameters in Edward Lorenz’s seminal work. (Spheres are colored according to the iteration count.) From certain angles, the two lobes of the attractor resemble a butterfly, a coincidence that helped earn sensitive dependence on initial conditions its nickname—the butterfly effect. An animated visualization of the attractor is available here. (Image courtesy of Stefan Ganev.)”




Photography by Juh-ku
-
 mercury49 liked this · 3 months ago
mercury49 liked this · 3 months ago -
 inbedwithsausage reblogged this · 3 months ago
inbedwithsausage reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 oww666 liked this · 3 months ago
oww666 liked this · 3 months ago -
 quarterturnthrottle reblogged this · 3 months ago
quarterturnthrottle reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 quarterturnthrottle liked this · 3 months ago
quarterturnthrottle liked this · 3 months ago -
 diecastdougout liked this · 3 months ago
diecastdougout liked this · 3 months ago -
 dangerouspostland liked this · 3 months ago
dangerouspostland liked this · 3 months ago -
 thedognme liked this · 3 months ago
thedognme liked this · 3 months ago -
 jo3l79 liked this · 3 months ago
jo3l79 liked this · 3 months ago -
 foghornleghorn54 reblogged this · 3 months ago
foghornleghorn54 reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 foghornleghorn54 liked this · 3 months ago
foghornleghorn54 liked this · 3 months ago -
 fiftythreefiftyone liked this · 3 months ago
fiftythreefiftyone liked this · 3 months ago -
 ihatefordfanpage reblogged this · 3 months ago
ihatefordfanpage reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 pinkthingmongerpickle liked this · 3 months ago
pinkthingmongerpickle liked this · 3 months ago -
 just-pics-i-like liked this · 3 months ago
just-pics-i-like liked this · 3 months ago -
 zrexdude liked this · 3 months ago
zrexdude liked this · 3 months ago -
 thorthethundergod liked this · 3 months ago
thorthethundergod liked this · 3 months ago -
 bobbi211 liked this · 3 months ago
bobbi211 liked this · 3 months ago -
 bmxbikerscep liked this · 3 months ago
bmxbikerscep liked this · 3 months ago -
 rbrainer liked this · 3 months ago
rbrainer liked this · 3 months ago -
 ratroddermetal liked this · 3 months ago
ratroddermetal liked this · 3 months ago -
 67rusty liked this · 3 months ago
67rusty liked this · 3 months ago -
 wolf-silver55 liked this · 3 months ago
wolf-silver55 liked this · 3 months ago -
 twinsrk liked this · 3 months ago
twinsrk liked this · 3 months ago -
 harshethic liked this · 3 months ago
harshethic liked this · 3 months ago -
 orangeman62 liked this · 3 months ago
orangeman62 liked this · 3 months ago -
 i-j0s liked this · 3 months ago
i-j0s liked this · 3 months ago -
 rick6six6 liked this · 3 months ago
rick6six6 liked this · 3 months ago -
 fuelalteredokie liked this · 3 months ago
fuelalteredokie liked this · 3 months ago -
 everyspringinaz reblogged this · 3 months ago
everyspringinaz reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 oroshimaru1974 liked this · 3 months ago
oroshimaru1974 liked this · 3 months ago -
 spider10thick liked this · 3 months ago
spider10thick liked this · 3 months ago -
 morbidrodz reblogged this · 3 months ago
morbidrodz reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 thadude4432 liked this · 1 year ago
thadude4432 liked this · 1 year ago -
 aosteve liked this · 1 year ago
aosteve liked this · 1 year ago -
 jeremylawson reblogged this · 1 year ago
jeremylawson reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 grumprod liked this · 2 years ago
grumprod liked this · 2 years ago -
 alanmcor liked this · 2 years ago
alanmcor liked this · 2 years ago -
 freeusebiker liked this · 2 years ago
freeusebiker liked this · 2 years ago -
 friends55 liked this · 2 years ago
friends55 liked this · 2 years ago -
 gary4205 reblogged this · 2 years ago
gary4205 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 gary4205 liked this · 2 years ago
gary4205 liked this · 2 years ago