Black- Eyed Squid

Black- eyed squid
Gonatus onyx
The Black-eyed Squid is roughly over one foot (35 am) and is found at depths as deep as 2500m. The female Black-eyed Squid works fiercely to protect her babies, by carrying around a patch of egg for six to nine months. When the eggs hatch, 2000 to 3000 babies are released into the ocean. However, this makes her vulnerable to predators.
Photocredit: http://tolweb.org/Gonatus+onyx/19769
More Posts from Bioluminescentoceangoddess and Others


Sea Gooseberry
Pleurobrachia pileus
The Sea Gooseberry is a comb jelly or ctenophore that has two enormous tentacles covered with adhesive cells. When tiny crustaceans, eggs, and larvae brush against the tentacles, the prey are stuck to them. The Sea Gooseberry draws the tentacles to its mouth, and it consumes the prey. These unique organisms can be found as deep as 750 m.


Sea elephant
Carinaria japonica
The Sea Elephant is a translucent sea snail that has a large muscular body and a tiny triangular shell. Its foot is used for crawling on the ground, and it can be transformed into a fin that is used for swimming. It is called the “sea elephant” because it has a small trunk in its mouth that is used to swallow prey. Furthermore, the Sea Elephant eats arrow worms and jellies.
Photo credit
https://bodegahead.blogspot.com/2014/12/carinaria-part-2.html
http://tolweb.org/Carinaria_japonica/28750


Cigar Comb Jelly
beroe forskalii
The Cigar Comb Jelly is a gelatinous ctenophore that is marveled by many due to its sparkling bioluminescence. It tends to elegantly float around 120 m in the ocean. It uses unique, hair-like structures called ctens to move horizontally in the ocean. It also swims in a spiral pattern before consuming zooplankton in the ocean.
Photo credit: https://www.wrobelphoto.com/gelatinouszooplankton/h25347306
https://www.flickr.com/photos/a_migotto/27227530815


Gulper Eel
Saccopharynx sp.
The Gulper Eel is known for its massive jaws, which are capable of swallowing prey whole. It’s stomach is also able to expand twice its size. It is found only in the deep see about 2000 to 3000 meters in depth.
Photo credit: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XRO0IjSoHGA
https://marinebiochemistrygc2018.weebly.com/deep-sea-adaptations


Giant Bell Jelly
Scrippsia pacifica
The Giant Belly Jelly has 256 tentacles attached to a gelatinous bell-shaped base. Like most cnidarians, the Giant Belly Jelly uses specialized stinging cells called nematocysts to catch its prey. When fish and other prey swim into its tentacles, the sensory projection on the cnidocyte (cell that holds the nematocysts) is activated. Then the nematocysts and barb are released, hitting the vulnerable prey and releasing a toxin into the prey’s body. The Giant Bell Jelly is found at 400 m in the ocean. It is related to the jellyfish, but it is categorized as a Hydrozoa (similar to the Portuguese- man-o-war)
https://vimeo.com/42551565
Photo Credit: https://www.pinterest.cl/pin/467107792572034837/
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/ivytech-bio1-1/chapter/phylum-cnidaria/
Dear ocean enthusiast and supporters,
Hi everyone, thank you for supporting my blog. I have gained over 500 followers and that is worth celebrating. I will try my best to post every day some of the amazing creatures that live in the deep ocean. Have a great night!
Pyrocystis fusiformis is a common plankton that produces bioluminescence. Not exactly a marine animal, but an amazing organism that produces bioluminescence. So, I thought it was worth sharing on this page.



Pyrocystis fusiformis
Pyrocystis Fusiformis is a marine dinoflagellate that is non-motile and has a short life cycle (5-7 days). When disturbed, the dinoflagellate displays vibrant, blue bioluminescence. The bioluminescence is design to startle grazers, or cause them to glow, making them more vulnerable to predators. During the day, it uses photosynthesis to produce its own food, and it produce bioluminescence at night. Furthermore, it fixes carbon from the ocean and produces oxygen for the marine animals that live there. All in all, I find this diamond shaped plankton to be unique and beautiful.
Photo credit: https://fineartamerica.com/featured/2-bioluminescence-of-pyrocystis-fusiformis-gerd-guentherscience-photo-library.html
https://exploringtheinvisible.com/2013/11/21/c-mould-new-acquisition-pyrocystis-fusiformis/
https://www.flickr.com/photos/13084997@N03/32823053106


Jewel Squid
Histioteuthis heteropsis
The Jewel Squid is covered in color-changing photophores that resemble sparkling gem stones. They also have a light-red coloration and are about 20 cm in length. They display a unique behavioral adaptation called diel migration. During the day, they stay at depths around 400-1200 m, and then surface during night (0-400m). This behavioral pattern is designed maximize feeding at night, and avoid predators during the day. The primary predator of the Jewel Squid is the Sperm Whale.
Photo credit: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/722827808920240115/
https://twitter.com/theoctonation/status/1168516522270253056
An amazing glowing ctenophore!


Bloody-belly comb jelly
Lampocteis cruentiventer
The Bloody-belly is a 16 cm ctenophore that is found at depths 700 m to 1200m. It is crimson red in color and appears black in the deep ocean. However, the jelly has the ability to emit a different color. Furthermore, it uses highly iridescent ctenes to propel through the water.
Photo credit: https://laughingsquid.com/bloody-belly-comb-jelly/
https://www.reddit.com/r/deepseacreatures/comments/2j1717/bloodbelly_comb_jelly_lampocteis_cruentiventer/


Pacific Viperfish
Chauliodus macouni
The Pacific Viperfish looks intimidating with its sharp, pointy teeth and large jaws. However, its body is small and elongated. It can be found at depths ranging from 250m to 4390m. The Pacific Viperfish long teeth are an unique adaptation designed to keep prey trapped, but it is dangerously close to its eyes. There have been instances when they have caught prey that are too large to swallow and it dies along with its last meal. The Pacific Viper also has photophores along its body and a light organ near its dorsal fin. These organs exhibit bioluminescence and help with attracting pray: as well as, communicating with mates and confuse predators. It is one of the most ferocious predators of the deep ocean.
Photo credit: https://www.science-rumors.com/top-20-pacific-viperfish-facts-to-know-what-this-creature-is/
https://goldfisho.com/everything-you-need-to-know-about-viperfish/
-
 q8p reblogged this · 1 year ago
q8p reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 q8p liked this · 1 year ago
q8p liked this · 1 year ago -
 mycellpics liked this · 1 year ago
mycellpics liked this · 1 year ago -
 mawsteeth liked this · 2 years ago
mawsteeth liked this · 2 years ago -
 darknovalatte liked this · 3 years ago
darknovalatte liked this · 3 years ago -
 nejniy-pulse liked this · 3 years ago
nejniy-pulse liked this · 3 years ago -
 astrotracksuitbattalion liked this · 3 years ago
astrotracksuitbattalion liked this · 3 years ago -
 windyboysworld liked this · 3 years ago
windyboysworld liked this · 3 years ago -
 low-level--00 reblogged this · 3 years ago
low-level--00 reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 low-level--00 liked this · 3 years ago
low-level--00 liked this · 3 years ago -
 melonisopod liked this · 3 years ago
melonisopod liked this · 3 years ago -
 killerhaku liked this · 3 years ago
killerhaku liked this · 3 years ago -
 ghastlyprinces liked this · 3 years ago
ghastlyprinces liked this · 3 years ago -
 tt-squid reblogged this · 3 years ago
tt-squid reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 creaturedeityendless liked this · 3 years ago
creaturedeityendless liked this · 3 years ago -
 vaguelyexistingcloud liked this · 3 years ago
vaguelyexistingcloud liked this · 3 years ago -
 staur-astrum liked this · 3 years ago
staur-astrum liked this · 3 years ago -
 firedjinni liked this · 3 years ago
firedjinni liked this · 3 years ago -
 tt-squid reblogged this · 3 years ago
tt-squid reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 ash-the-nekogirl liked this · 3 years ago
ash-the-nekogirl liked this · 3 years ago -
 edgeworst reblogged this · 3 years ago
edgeworst reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 salvagethevixin liked this · 3 years ago
salvagethevixin liked this · 3 years ago -
 diminishedtobe liked this · 4 years ago
diminishedtobe liked this · 4 years ago -
 110car8s liked this · 4 years ago
110car8s liked this · 4 years ago -
 idkawtd liked this · 4 years ago
idkawtd liked this · 4 years ago -
 dharmabeatdownblog reblogged this · 4 years ago
dharmabeatdownblog reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 gin-n reblogged this · 4 years ago
gin-n reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 universalstudent reblogged this · 4 years ago
universalstudent reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 universalstudent liked this · 4 years ago
universalstudent liked this · 4 years ago -
 hidradigital reblogged this · 4 years ago
hidradigital reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 roastpatato reblogged this · 4 years ago
roastpatato reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 roastpatato liked this · 4 years ago
roastpatato liked this · 4 years ago -
 boobger reblogged this · 4 years ago
boobger reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 boobger liked this · 4 years ago
boobger liked this · 4 years ago -
 expectoprotronads liked this · 4 years ago
expectoprotronads liked this · 4 years ago -
 lemonjamtart reblogged this · 4 years ago
lemonjamtart reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 lemonjamtart liked this · 4 years ago
lemonjamtart liked this · 4 years ago -
 bardoon-official liked this · 4 years ago
bardoon-official liked this · 4 years ago -
 lilylizard reblogged this · 4 years ago
lilylizard reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 lizard-city liked this · 4 years ago
lizard-city liked this · 4 years ago -
 chlorr-no-face reblogged this · 4 years ago
chlorr-no-face reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 ninjakitten96 liked this · 4 years ago
ninjakitten96 liked this · 4 years ago -
 lipid reblogged this · 4 years ago
lipid reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 woodcutchimera reblogged this · 4 years ago
woodcutchimera reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 hungwy liked this · 4 years ago
hungwy liked this · 4 years ago
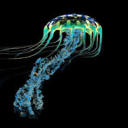
Bioluminescence is a chemical reaction that produces light. Many deep sea animals use bioluminescence. This blog is dedicated to educating the public about the amazing creatures that thrive in the deep sea.
57 posts